Thanks!!
This Is Pictures.
Collapse
X
-
-
 Transaction Feedback: -click here
Transaction Feedback: -click here
[e30: '91 318is coupe|brilliantrot||e36: '98 318ti|fern green|California top|M-Tech]
[URL="http://www.r3vlimited.com/board/showthread.php?t=300453"]Comment
-
-
Our universe is a beautiful, confounding thing...
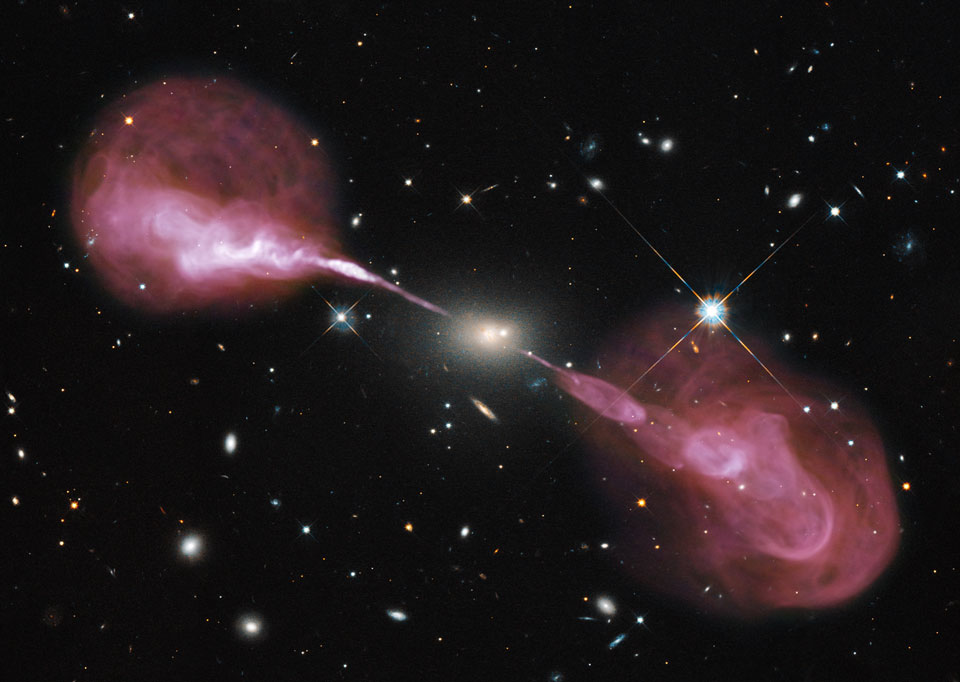

Explanation: Why does this galaxy emit such spectacular jets? No one is sure, but it is likely related to an active supermassive black hole at its center. The galaxy at the image center, Hercules A, appears to be a relatively normal elliptical galaxy in visible light. When imaged in radio waves, however, tremendous plasma jets over one million light years long appear. Detailed analyses indicate that the central galaxy, also known as 3C 348, is actually over 1,000 times more massive than our Milky Way Galaxy, and the central black hole is nearly 1,000 times more massive than the black hole at our Milky Way's center. Pictured above is a visible light image obtained by the Earth-orbiting Hubble Space Telescope superposed with a radio image taken by the recently upgraded Very Large Array (VLA) of radio telescopes in New Mexico, USA. The physics that creates the jets remains a topic of research with a likely energy source being infalling matter swirling toward the central black hole.
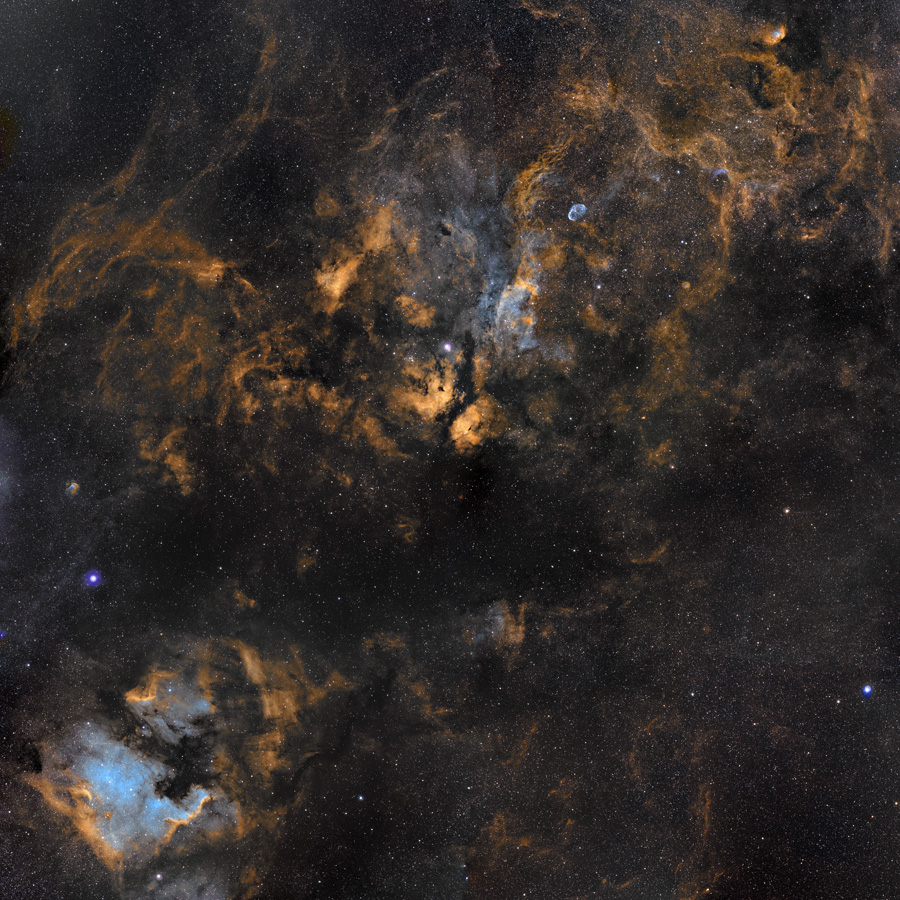

Explanation: Cosmic clouds of gas and dust drift across this magnificent mosaic covering a 12x12 degree field within the high flying constellation Cygnus. The collaborative skyscape, a combination of broad and narrow band image data presented in the Hubble palette, is anchored by bright, hot, supergiant star Deneb, below center near the left edge. Alpha star of Cygnus, Deneb, is the top of the Northern Cross asterism and is seen here next to the dark void known as the Northern Coal Sack. Below Deneb are the recognizable North America and Pelican nebulae (NGC 7000 and IC 5070). Another supergiant star, Sadr (Gamma Cygni) is near the center of the field just above the bright wings of the Butterfly Nebula. A line continuing up and right will encounter the more compact Crescent Nebula and finally the Tulip Nebula near the top of the frame. Most of these complex nebulosities are located about 2,000 light-years away. Along with the Sun, they lie in the Orion spiral arm of our Milky Way galaxy.
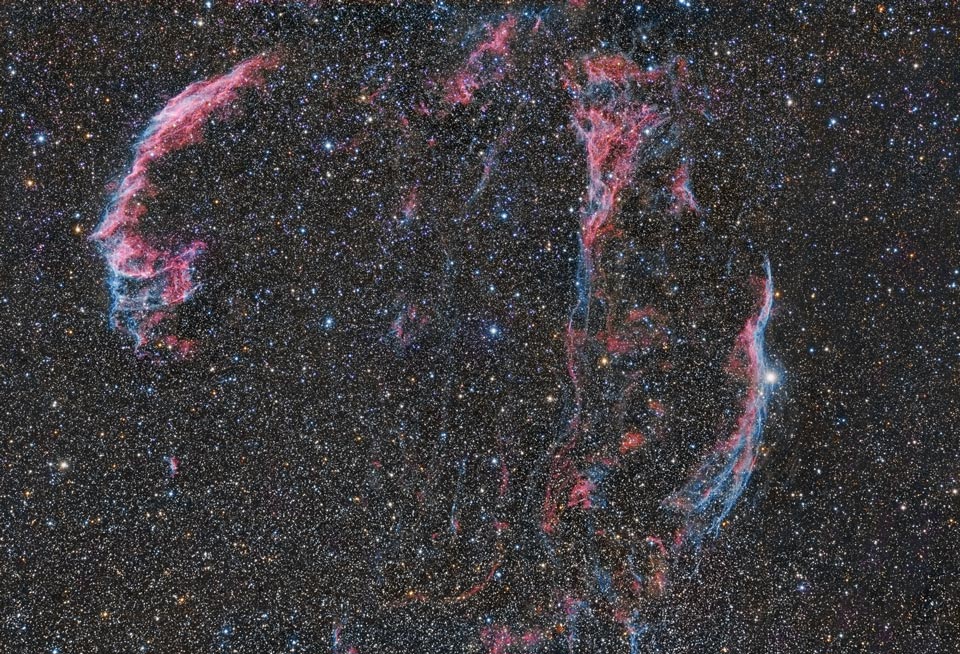

Explanation: Wisps like this are all that remain visible of a Milky Way star. About 9,000 years ago that star exploded in a supernova leaving the Veil Nebula, also known as the Cygnus Loop. At the time, the expanding cloud was likely as bright as a crescent Moon, remaining visible for weeks to people living at the dawn of recorded history. Today, the resulting supernova remnant has faded and is now visible only through a small telescope directed toward the constellation of the Swan (Cygnus). The remaining Veil Nebula is physically huge, however, and even though it lies about 1,400 light-years distant, it covers over five times the size of the full Moon. In images like this of the complete Veil Nebula, studious readers should be able to identify several of the individual filaments. A bright wisp at the right is known as the Witch's Broom Nebula.
Mars:
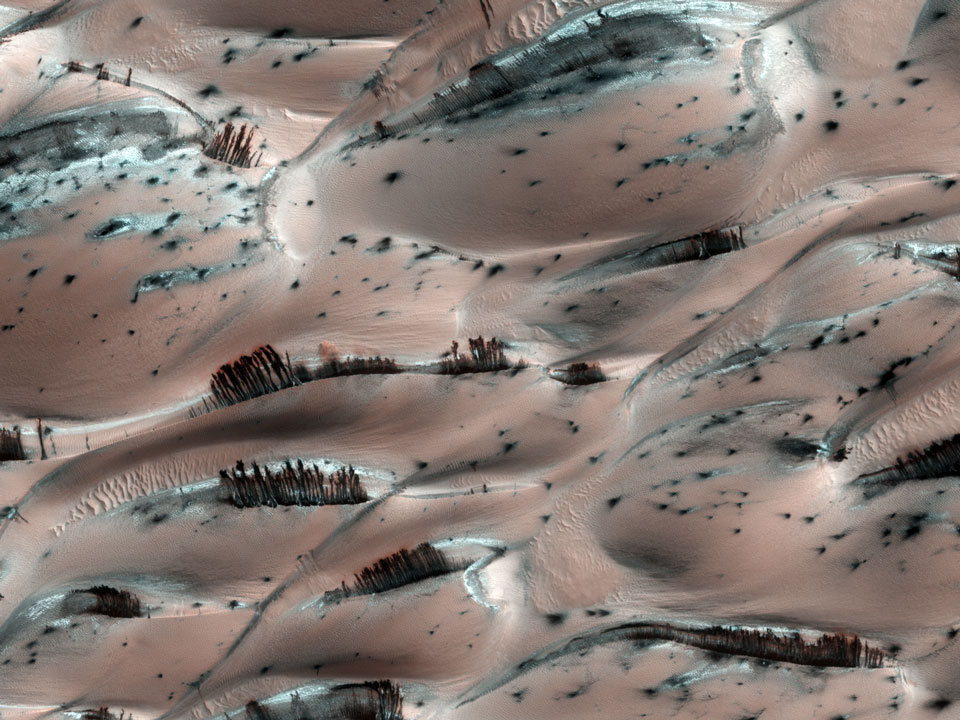

Explanation: They might look like trees on Mars, but they're not. Groups of dark brown streaks have been photographed by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on melting pinkish sand dunes covered with light frost. The above image was taken in 2008 April near the North Pole of Mars. At that time, dark sand on the interior of Martian sand dunes became more and more visible as the spring Sun melted the lighter carbon dioxide ice. When occurring near the top of a dune, dark sand may cascade down the dune leaving dark surface streaks -- streaks that might appear at first to be trees standing in front of the lighter regions, but cast no shadows. Objects about 25 centimeters across are resolved on this image spanning about one kilometer. Close ups of some parts of this image show billowing plumes indicating that the sand slides were occurring even when the image was being taken.
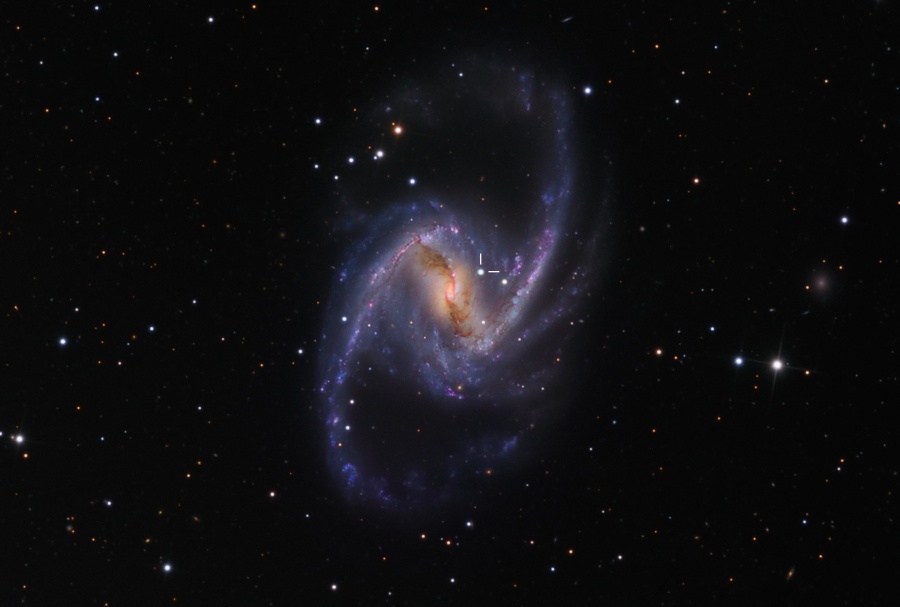

Barred spiral galaxy NGC 1365 is truly a majestic island universe some 200,000 light-years across. Located a mere 60 million light-years away toward the chemical constellation Fornax, NGC 1365 is a dominant member of the well-studied Fornax galaxy cluster. This sharp color image shows intense star forming regions at the ends of the bar and along the spiral arms, and details of dust lanes cutting across the galaxy's bright core. At the core lies a supermassive black hole. Astronomers think NGC 1365's prominent bar plays a crucial role in the galaxy's evolution, drawing gas and dust into a star-forming maelstrom and ultimately feeding material into the central black hole. Discovered on October 27, the position of a bright supernova is indicated in NGC 1365. Cataloged as SN2012fr, the type Ia supernova is the explosion of a white dwarf star.
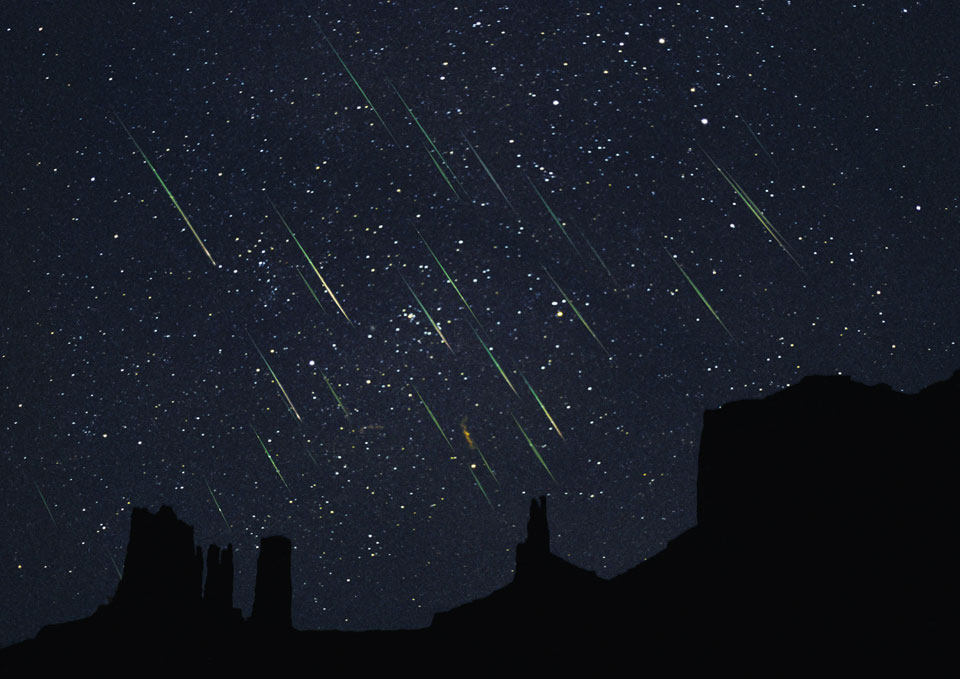

Explanation: What's happening in the sky over Monument Valley? A meteor shower. Over the past weekend the Leonid meteor shower has been peaking. The image -- actually a composite of six exposures of about 30 seconds each -- was taken in 2001, a year when there was a much more active Leonids shower. At that time, Earth was moving through a particularly dense swarm of sand-sized debris from Comet Tempel-Tuttle, so that meteor rates approached one visible streak per second. The meteors appear parallel because they all fall to Earth from the meteor shower radiant -- a point on the sky towards the constellation of the Lion (Leo). Although the predicted peak of this year's Leonid meteor shower is over, another peak may be visible early tomorrow morning. By the way -- how many meteors can you identify in the above image?
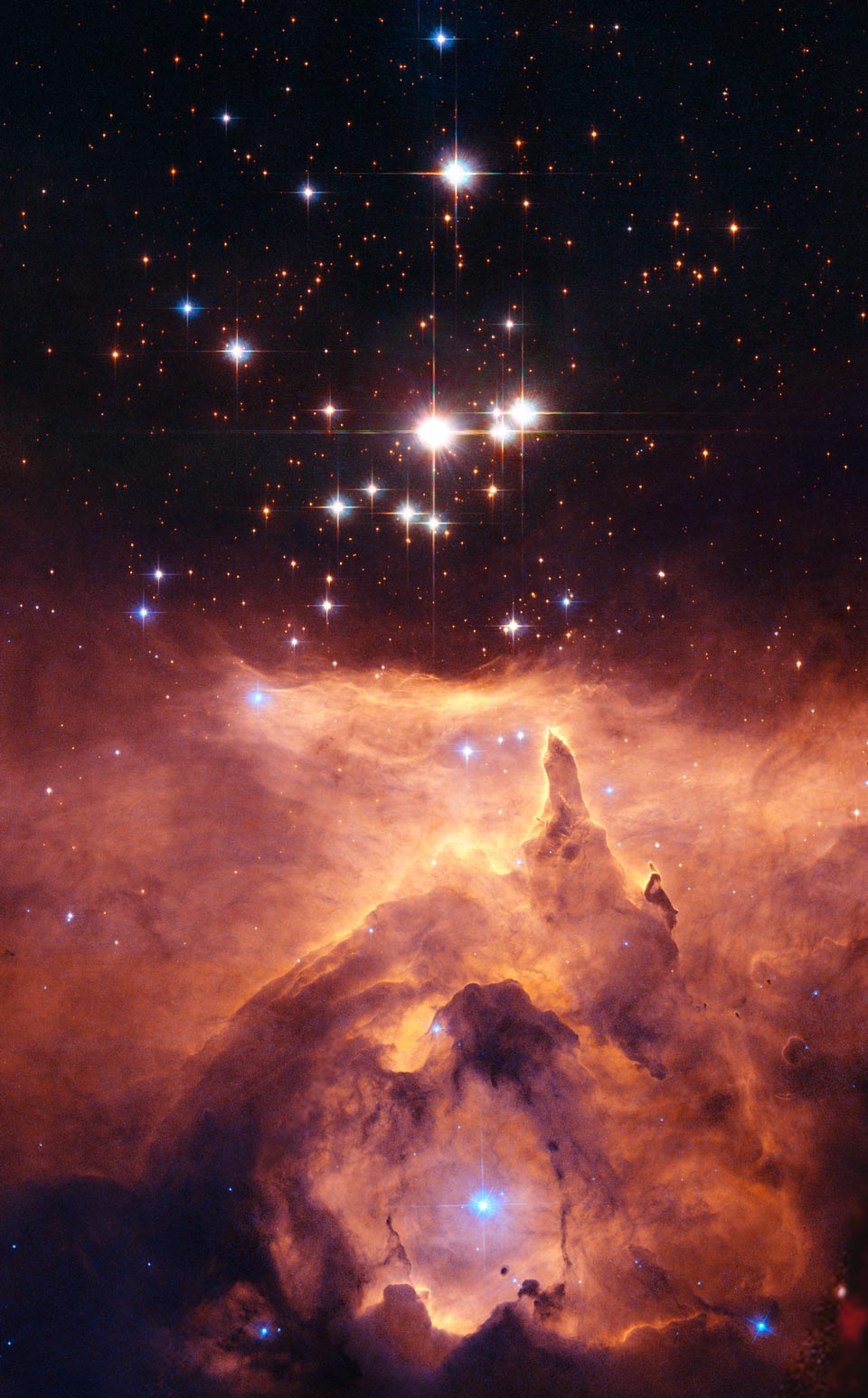

Explanation: How massive can a normal star be? Estimates made from distance, brightness and standard solar models had given one star in the open cluster Pismis 24 over 200 times the mass of our Sun, nearly making it the record holder. This star is the brightest object located just above the gas front in the above image. Close inspection of images taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, however, have shown that Pismis 24-1 derives its brilliant luminosity not from a single star but from three at least. Component stars would still remain near 100 solar masses, making them among the more massive stars currently on record. Toward the bottom of the image, stars are still forming in the associated emission nebula NGC 6357. Appearing perhaps like a Gothic cathedral, energetic stars near the center appear to be breaking out and illuminating a spectacular cocoon.
Look at all of those galaxies...
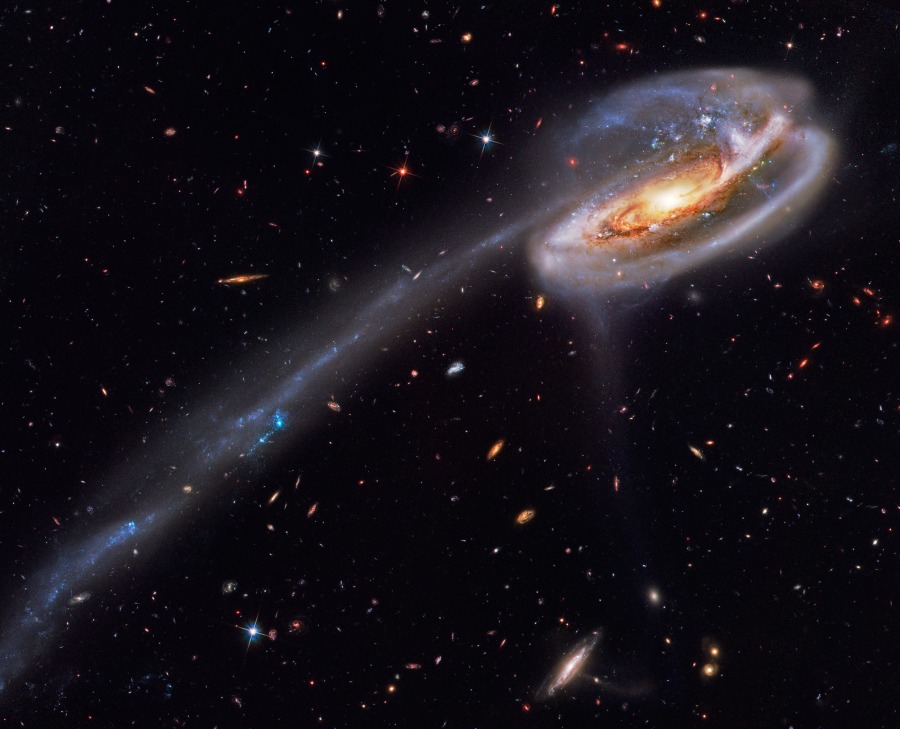

Explanation: In this stunning vista, based on image data from the Hubble Legacy Archive, distant galaxies form a dramatic backdrop for disrupted spiral galaxy Arp 188, the Tadpole Galaxy. The cosmic tadpole is a mere 420 million light-years distant toward the northern constellation Draco. Its eye-catching tail is about 280 thousand light-years long and features massive, bright blue star clusters. One story goes that a more compact intruder galaxy crossed in front of Arp 188 - from right to left in this view - and was slung around behind the Tadpole by their gravitational attraction. During the close encounter, tidal forces drew out the spiral galaxy's stars, gas, and dust forming the spectacular tail. The intruder galaxy itself, estimated to lie about 300 thousand light-years behind the Tadpole, can be seen through foreground spiral arms at the upper right. Following its terrestrial namesake, the Tadpole Galaxy will likely lose its tail as it grows older, the tail's star clusters forming smaller satellites of the large spiral galaxy.
EDIT: If you're an astronomy/astrophysics nerd like myself, you can check out where I got all of those photos. NASA has a really cool "Photo of the day" website where they post the photos and explanations. See it at: http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/archivepix.html
Comment
-
Question:
It looks as though the back wheels are spinning (I dont see the silver screws on the rear wheels). There is no one in the front seat though. Are the wheels not spinning, or has there been some fancy pantsy editing going on?
Also, those space picks are nuts. the incredibility of space hit me while looking at them that the stars in the sky are FUCKING SUNS MILLIONS OF MILES AWAY MILLIONS OF YEARS AGO. That's just fucking nuts.
No i am not high.Comment
-
Our universe is a beautiful, confounding thing...
*space*
EDIT: If you're an astronomy/astrophysics nerd like myself, you can check out where I got all of those photos. NASA has a really cool "Photo of the day" website where they post the photos and explanations. See it at: http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/archivepix.html
as a newly initiated space nerd, i thank you many times over. such a sublimely unknown realm we inhabit..Comment
-
Comment
-
Then you know how incredible what exists inside our own bodies. Scale wise, we're at the middle of the spectrum. The smallest particles which make up the atoms in our bodies are as distant by scale as the largest objects which compose the universe, clusters of galaxies. The universe is big yes, but we're by no means small either.EDIT: If you're an astronomy/astrophysics nerd like myself, you can check out where I got all of those photos. NASA has a really cool "Photo of the day" website where they post the photos and explanations. See it at: http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/archivepix.htmlComment
-
-
Comment
-









Comment